Description
The thyroid gland produces two hormones, tyroxine (also called T4) and tri-iodothyronine (also called T3). T4 is produced and circulated in greater quantities than is T3, which is more active than T4. Although T4 has a clear function, it should be considered as a pro-hormone of T3, which is synthesised from T4. The thyroid hormones are essential for body metabolism; they stimulate the consumption of oxygen in every body cell, which leads to the production of heat.
When hypo- (too slow) or hypert- (too fast) thyriod function is suspected, the levels of TSH, T3 and/or T4 in the blood are usually measured. However, in practice, the level of T3 (and T4) in 24-hour urine shows better correlation with the symptoms, particularly in early stage hypothyroidism. When symptoms indicative of mild hypothyroidism are present, hormone levels measured in 24-hour urine will confirm the condition, though blood values may still be normal. Therefore, this test is particularly suitable when hypothyroidism has not yet been confirmed by routine blood tests.
Several scientists have expressed a suspicion that an increasingly significant percentage of the population suffers from subclinical hypothyroidism, which occurs much more frequently than originally thought.
Further information
The thyroid gland is stimulated to produce T3 from T4 by Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH), which is produced by the pituitary gland. The production TSH is in turn stimulated by Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH), which is produced by the hypothalamus. T3 and, to a lesser extent, T4 inhibit the formation of both TSH and TRH via negative feedback.
The formation of TSH is stimulated by cold, and inhibited by heat as well as by certain stressful situations. Thyroid function can be negatively affected by low adrenal function, malnutrition (eg iodine and tyrosine) and ageing. The conversion of T4 to T3 can be negatively affected by ageing, malnutrition (e.g. selenium, zinc and copper deficiency), low adrenal function, beta-blockers and the contraceptive pill.
In addition to T3, T4 can also be converted into rT3 (3,3,5 tri-iodothyronine or reverse T3). This hormone is not biologically active and reduces the activity of T3. Conversion into one form of T3 over the others allows the body additional flexibility possibility to regulate body metabolism, such as in hyper- or hypothyroidism. As would be expected, the T3/rT3 ratio is high in hyperthyroidism (more T3), and low in hypothyroidism (less T3).
Non-thyroid related disorders can also decrease the T3/rT3 ratio, which may cause signs of hypothyroidism. A reduced T3/rT3 ratio was found, among other things, after fasting, stress, liver cirrhosis and insulin-dependent diabetes.
In the T3 and T4 tests in 24-hour urine, not only are the levels of T3 and T4 measured but their ration is also calculated. The T3/T4 ratio gives information about the degree of conversion of T4 to T3. In addition, cortisol, and cortisol metabolites (17-hydroxysteroids) can be determined in 24-hour urine.
When is it usefull to determine thyroid hormones T3 and T4 in 24-hour urine?
It is useful to test for T3 and T4 in 24-hour urine in the case of hypothyroid symptoms, when the blood values are normal. This test can also be used to check the effect of an adopted therapy.
Symptoms that may indicate hypothyroidism are:
Coldness (cold extremities)
Fatigue (especially in the morning)
Low basal body temperature (<36.7 C)
Low peristalsis and constipation
Headache
Mix-oedema (fluid retention)
Decreased appetite
Dry skin
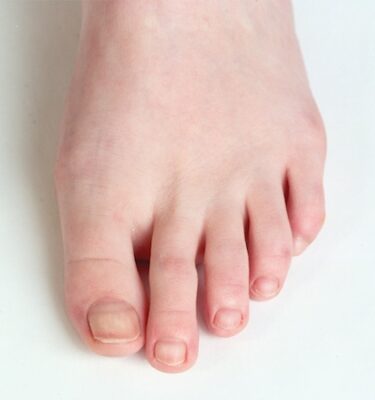
Brittle nails
Dry, coarse, slowly growing hair
Muscle and joint pain
Weight gain
Deafness and tinnitus
Prone to infections (mainly of the airways)
Hoarseness
Extended Achilles tendon reflex
Mental/nervous symptoms
Apathy
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Slowness/sluggishness
Distraction
Memory impairment
Nervousness
Depression
Irritability